Stem Cells Regenerative Medicine. The term “stem cells” originates from the word “stem,” signifying the trunk of a tree. Hence often referred to as “somatic cells.” It’s crucial to highlight the unique ability of these cells to undergo asymmetric division, resulting in two daughter cells. One retains the original stem cell properties. While the other can differentiate under suitable environmental conditions, a process known as self-renewal.
Adult tissues in organisms typically harbor a resident population of adult stem cells. Facilitating periodic renewal or regeneration following tissue damage. Notably, certain adult stem cells, like mesenchymal stem cells and hematopoietic stem cells, can differentiate into multiple cell types. Others serve as direct precursors to cells within their residing tissue, such as skin, muscle, intestinal, or gonadal stem cells.
Embryonic stem cells, part of the inner cell mass of 4-5 day-old embryos, are pluripotent. This means they can generate all three germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm, laying the foundation for various body tissues and organs.
Ectoderm: The Outer Layer
The ectoderm, the embryo’s outermost layer, forms first during the blastula phase and later gives rise to the other two layers through gastrulation. This layer is pivotal in developing the nervous system and skin.
Mesoderm: The Middle Layer
The mesoderm, or the intermediate layer, forms various body structures, including the musculoskeletal system and other vital organs, during gestation.
Endoderm: The Inner Layer
The endoderm, the innermost germ layer, is instrumental in forming the digestive and respiratory systems’ cellular and tissue structures, along with glands like the thyroid and pancreas, and organs such as the liver.
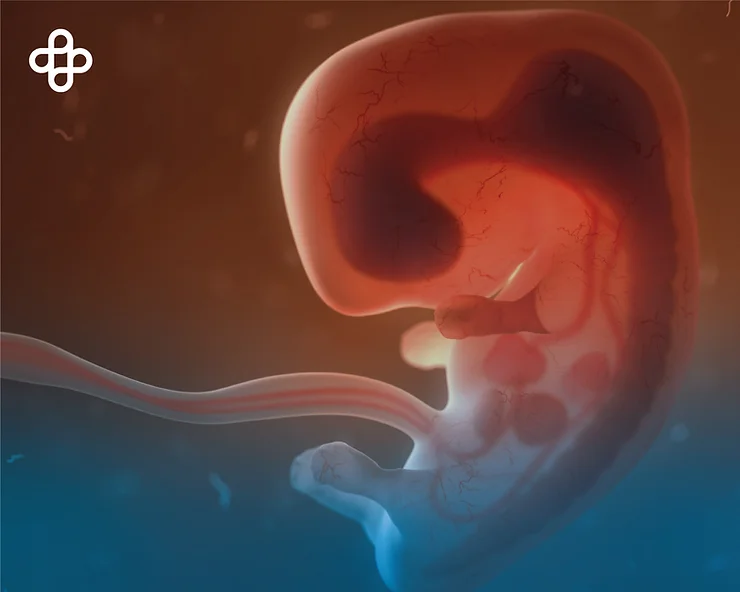
A key feature of embryonic stem cells is their indefinite maintenance in culture under specific conditions, ensuring a stable population of stem cells. Experimental techniques now exist to derive embryonic stem cells without destroying the embryo, marking a significant advance in regenerative medicine.
Expanding the Horizon of Regenerative Medicine
The field of regenerative medicine stands on the brink of revolutionizing healthcare, offering hope for incurable diseases and damaged tissues. As noted by the National Institutes of Health. “Stem cells have the remarkable potential to develop into many different cell types in the body. During early life and growth”. This versatility underpins their role in developing novel therapeutic strategies, from regenerating damaged heart tissue to treating neurological disorders.
Conclusions: The Future is Now
The exploration and utilization of stem cells embody the fusion of science, ethics, and innovation. Driving forward the boundaries of what is medically possible. Their capacity for differentiation and self-renewal opens up new avenues for understanding human development, disease mechanisms, and the creation of targeted treatments. As research advances and ethical considerations are navigated, the potential of stem cells to transform regenerative medicine and offer new hope to millions continues to unfold. The journey of stem cells from bench to bedside exemplifies the dynamic interplay between scientific discovery and its application to human health, marking a new era in medical science.
Finally, If you want to know more, visit our article on What Are Stem Cells.