Thyroid Gland: Its Functions and Disorders
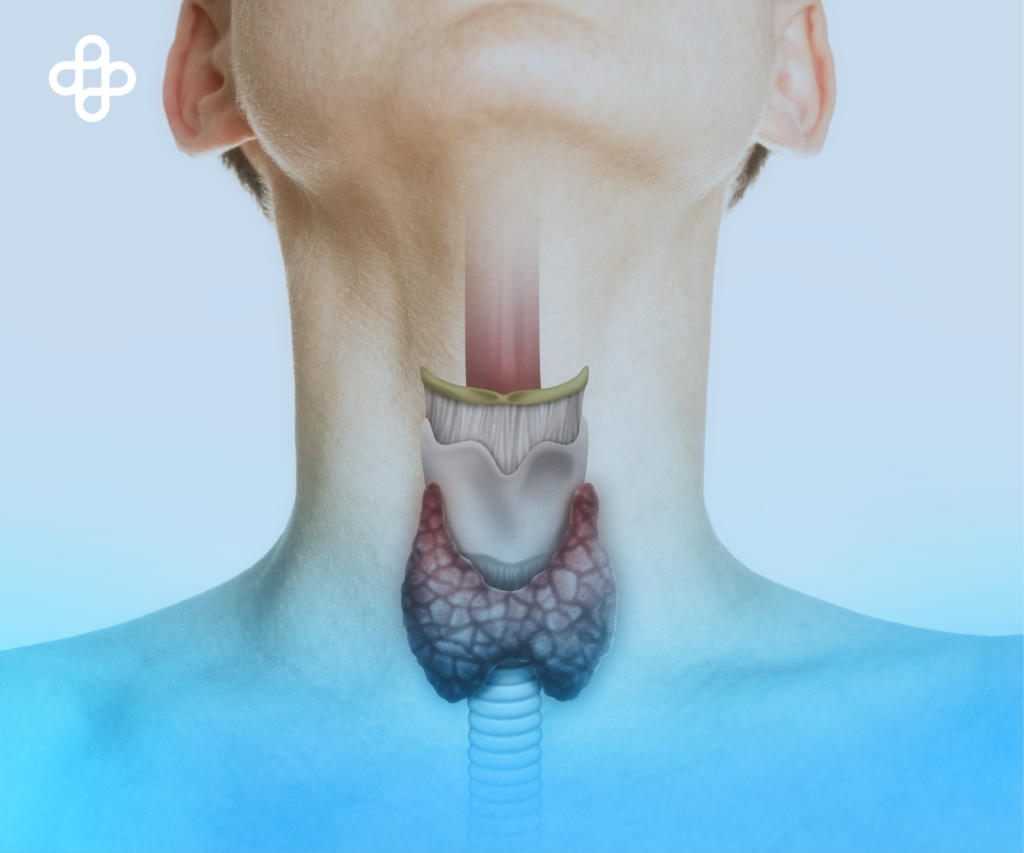
What is the Thyroid? The thyroid is an endocrine gland, resembling a butterfly in shape, located at the base of the neck, just below the Adam’s apple (thyroid cartilage).
Functions of the Thyroid Gland
The thyroid gland produces, stores, and releases thyroid hormones into the bloodstream. These hormones influence the activity of nearly every cell in the body and regulate metabolism. The thyroid gland’s function is controlled by another gland, the pituitary gland, which is in turn controlled by the hypothalamus located in the brain. In case the thyroid hormone levels are insufficient, the hypothalamus and pituitary gland initiate mechanisms to increase the synthesis and release of T3 and T4 into the bloodstream. Conversely, if an excess of these hormones is detected, their release is reduced. These mechanisms can be altered in case of illness.
Metabolic Functions
The thyroid gland plays a crucial role in various metabolic functions, including:
- Accelerating or slowing down heart rate.
- Regulating nutrient assimilation (affecting weight gain and loss).
- Adjusting body temperature.
- Controlling the speed of food movement through the digestive tract.
- Regulating the pace of cell replacement.
- Influencing glucose synthesis and usage.
Role of Iodine and Thyroid Hormones
The thyroid gland uses dietary iodine and combines it with tyrosine to synthesize the mentioned thyroid hormones. These hormones circulate freely or bound to proteins in the bloodstream and eventually reach thyroid receptors. Importantly, the thyroid and pituitary glands work in tandem. The pituitary gland releases thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which stimulates the thyroid to synthesize T3 and T4 hormones.
Hypothyroidism: An Underactive Thyroid
Hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland fails to produce adequate thyroid hormones. This condition is also known as an underactive thyroid. In the early stages, hypothyroidism might not cause noticeable symptoms. However, untreated hypothyroidism can lead to other health issues over time, such as high cholesterol or heart problems. The most common cause of hypothyroidism is an autoimmune disease called Hashimoto’s disease.
Hyperthyroidism: An Overactive Thyroid
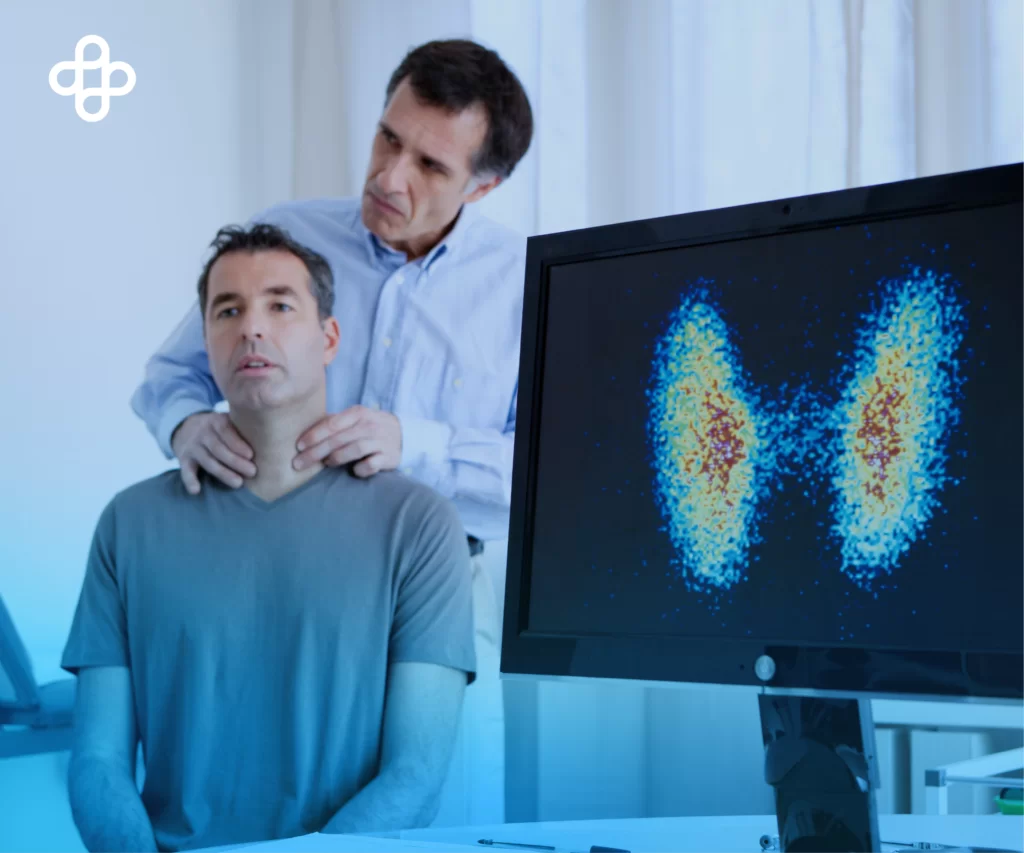
Hyperthyroidism involves excessive thyroid hormone levels in the body. The most common cause is Graves’ disease, an autoimmune disorder where the body produces antibodies that stimulate the thyroid to produce more thyroid hormones. Symptoms and the appearance of goiter, along with elevated T4 and T3 levels in the blood, often point towards hyperthyroidism.

Thyroid Disorders
There are several thyroid disorders with various triggers, including:
- Firstly, Hyperthyroidism, also known as an overactive thyroid.
- Secondly, Hypothyroidism, or underactive thyroid.
- Thirdly, Malignant tumor growth in thyroid tissue characterizes thyroid cancer.
- fourthly, Nodules, which can lead to hyperthyroidism.
- the last one is Goiter, the enlargement of the thyroid gland.
Interconnected Thyroid Disorders
Many thyroid disorders are interconnected. For instance, nodules can cause hyperthyroidism, but they can also present as a standalone condition. These conditions manifest with general and nonspecific signs and symptoms, making specific tests crucial for accurate diagnosis in case of prolonged discomfort.
Explore Advances in Thyroid Research and Stem Cells Discover the latest breakthroughs in thyroid research and their connection to stem cells.
Spanish Version of Thyroid Gland: Its Functions and Disorders