Stem Cell Applications in Modern Medicine. When discussing the therapeutic applications of stem cells, it’s essential to consider the future and probability. Initially, stem cells are thought to hold numerous and diverse potential uses in medicine, primarily aimed at immunotherapy, gene therapy, and what is known as regenerative therapy.
“Stem cells have the remarkable potential to develop into many different cell types in the body during early life and growth.”
National Institutes of Health
Current Uses of Stem Cells
Researchers currently use stem cells to treat some diseases, nearly all of which are still experimental. The field that has seen the most advancement, or at least has the most published clinical studies, involves the use of umbilical cord blood in treating certain leukemias, lymphomas, other types of cancer, and hematological diseases.
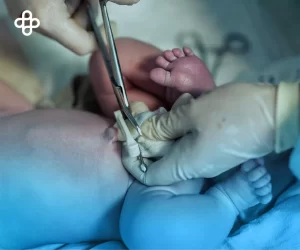
Transfusion Processes and Rejection Rates
Doctors perform these treatments by transfusing the child suffering from the disease, who is also the donor, thereby eliminating the possibility of rejection.
Research Advances in Animal Models
Research is now developing in animal models using stem cells extracted from umbilical cord blood or obtained through other means, such as the genetic reprogramming of somatic cells.
Laboratory Monitoring
In the laboratory, scientists can monitor stem cells as they divide and become increasingly specialized, giving rise to skin, bone, brain, and other types of cells.
Potential Applications in Animal Experiments
Animal experiments have shown very promising results in treating diseases like type 1 diabetes, spinal cord injuries, Parkinson’s disease, and cardiovascular incidents like heart attacks, as well as diseases involving neuron destruction and hematological conditions. However, in many cases, researchers must still confirm these results in humans.

Focus on Cellular Therapy
Researchers currently focus most of their efforts on cellular therapy in the clinical applications of stem cells. This process involves cultivating or regenerating tissues to repair damaged ones or, in the case of organs, those that are malfunctioning. Experimental treatments for cancer or cardiac diseases are underway, but this is just the beginning of a long journey.
Bone Marrow Transplantation
It should be noted that the precursor to these types of therapies has been bone marrow transplantation, generally applied to treat certain types of hematological cancers, such as leukemia, some solid tumors, and other blood and metabolic diseases.
Umbilical Cord Blood Stem Cells
In this case, it is the adult stem cells, capable of producing blood and lymphatic cells, that do the work. The availability of umbilical cord blood, which provides pluripotent stem cells, is transforming the landscape of clinical research. This applies whether it is for autologous use, when stored in a private bank, or to provide to compatible individuals if preserved in a public bank.
Advantages of Adult Stem Cells
Adult stem cells provide the advantage of avoiding rejection because they come directly from the patient. Otherwise, there is a clear risk of rejection.
Challenges and Future Directions
Many issues still need resolution before these types of therapies can become a reality. However, there is no doubt that the future of medicine lies in stem cells. Besides transplantation, researchers direct their study of stem cells toward potential treatment applications. Diseases such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, cardiovascular diseases, and cancer. Including those caused by genetic errors, as they are supposed to allow the introduction of genetically programmed stem cells into damaged tissues to generate healthy tissue that replaces the sick one.
Thereafter, be sure to visit our article What are stem cells?
Stem Cell Applications in Modern Medicine