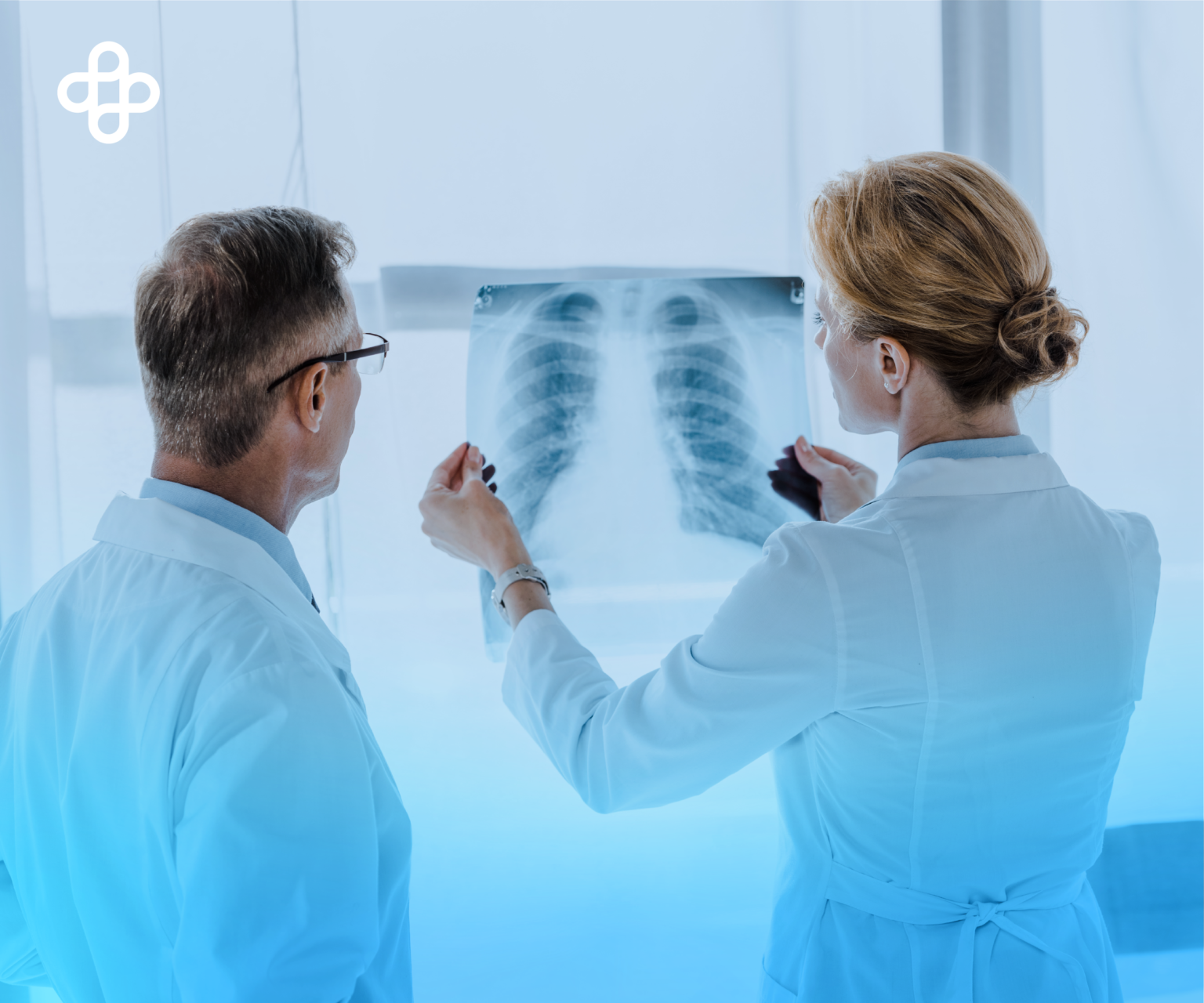
Chronic pneumonia poses a significant public health challenge, affecting millions globally. Advances in regenerative medicine have introduced groundbreaking opportunities for managing severe respiratory conditions like chronic pneumonia using stem cell therapies. These innovative treatments show immense promise in reducing inflammation, repairing damaged lung tissue, and enhancing patients’ quality of life.
What Is Chronic Pneumonia?
Chronic pneumonia is a prolonged inflammatory condition of the lungs. Unlike acute pneumonia, which resolves with treatment, chronic pneumonia can lead to lasting lung damage, characterized by persistent coughing, breathing difficulties, and extreme fatigue. Traditional treatments, such as antibiotics and steroids, often fall short, particularly in severe cases. This is where regenerative therapies, especially those using stem cells, provide new hope.
The Role of Stem Cells in Lung Regeneration
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have emerged as the cornerstone of regenerative treatments for chronic pneumonia. These cells, known for their ability to differentiate into various cell types, are pivotal in repairing and regenerating damaged lung tissue. Research shows that MSCs not only regenerate lung epithelial cells but also modulate immune responses, significantly reducing the inflammation responsible for pulmonary deterioration.

How Stem Cells Work
Stem cells employed in treating chronic pneumonia function in several ways:
- Inflammation Reduction: MSCs release anti-inflammatory cytokines that mitigate the excessive inflammatory response damaging lung tissue.
- Tissue Repair: They promote the regeneration of lung epithelial cells, aiding the repair of damaged tissues.
- Immune System Modulation: MSCs suppress overactive immune responses that exacerbate the condition, restoring immune balance in the lungs.
Clinical Trials and Scientific Evidence
Clinical trials worldwide are exploring the potential of stem cells in chronic pneumonia treatment. A study published in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine reported significant improvements in lung function and symptom severity in patients treated with MSCs. Additionally, a 2023 analysis highlighted the potential of stem cell therapies to decrease dependence on mechanical ventilation in severe cases.
In another trial, MSCs were administered to patients with chronic pneumonia and pulmonary fibrosis. Preliminary findings indicated marked improvements in lung capacity and slowed fibrosis progression, suggesting the potential of stem cell therapies as a long-term treatment option.
Benefits and Risks of Stem Cell Therapies
Stem cell therapies hold great promise, but like any innovative treatment, they come with potential risks. These include the possibility of improper integration into lung tissue or adverse immune reactions. However, ongoing advancements in medical technology continuously refine treatment protocols to minimize risks and maximize benefits for patients.
Future Directions in Regenerative Medicine for Respiratory Diseases
Regenerative medicine is evolving rapidly, with stem cells at its core. In the coming years, therapies combining stem cells with emerging technologies like tissue engineering and gene therapy are expected to provide more effective and personalized solutions for chronic pneumonia and other severe lung diseases. Additionally, research into stem cells derived from adipose tissue and umbilical cords is expanding, offering less invasive and more accessible treatment options.
Conclusion
Chronic pneumonia remains a debilitating disease, but regenerative medicine, particularly stem cell therapy, is reshaping its treatment landscape. With ongoing research and clinical trials, stem cell-based treatments could soon become the gold standard for managing chronic lung diseases, offering unprecedented hope to patients worldwide.
Visit our article How Stem Cell Therapy Can Revolutionize Treatment for COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)