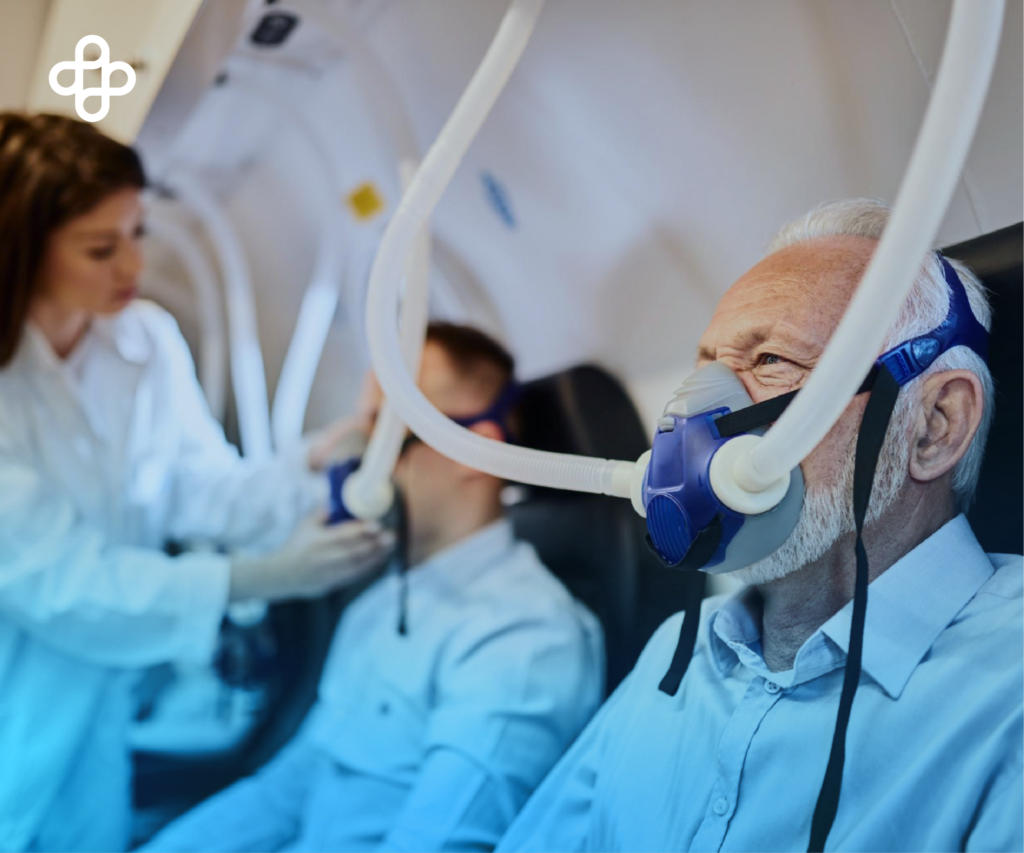
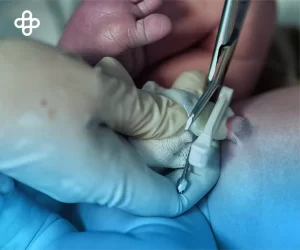
“How to Breathe Better Using Stem Cells?” is one of the most common questions in consultations at Eternal Medical Center. Stem cell-based therapies are currently under investigation. Therapeutic results are very promising for a number of incurable and degenerative lung diseases.
For example, At Eternal Medical Center in Monterrey. Mexico, we always strive to keep our patients well-informed and up-to-date about these new medical trends. Our goal is to instill greater confidence in the available opportunities with regenerative medicine.
What is Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)?
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a group of lung diseases that make breathing difficult and worsen over time. Medical professionals use this term to describe progressive lung diseases. For example, emphysema, chronic bronchitis, refractory asthma, and certain forms of bronchiectasis. Patients with this disease experience a progressive increase in the sensation of shortness of breath. This leads to reduced lung function and, in many cases, respiratory failure.
According to the World Health Organization, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is the third leading cause of death worldwide. It caused 3.23 million deaths in 2019 alone. In Mexico, 86 percent of cases remain underdiagnosed. In our region, the disease claims 20,000 lives every year. Dr. Alejandra Ramírez Venegas, from the National Institute of Respiratory Diseases “Ismael Cosío Villegas” warns. Published an article in the Gazette of the Faculty of Medicine of the UNAM.
In Estoril, Portugal, on March 25, 2017, at the European Respiratory Society Lung Science Conference. Mesenchymal stem cells were used, which are multipotent cells that can differentiate into a variety of cells obtained from adipose tissue and bone marrow, for example.

The Study
Researchers administered mesenchymal stem cells intravenously to mice at 4 and 6 weeks of age, and they collected tissue and lung cell samples.
The researchers compared these findings with a control group that did not receive mesenchymal stem cell treatment. The results showed a significant reduction in inflammation in the group that received stem cell therapy.
Analysis of the lung tissue revealed a decrease in lung destruction in specific lung areas in mice treated with stem cells. In addition to reducing lung inflammation, stem cell therapy also led to significant improvements in lung structure, suggesting that this form of treatment has the potential to repair damaged lungs.
These results demonstrate the potential effectiveness of stem cell treatment as a means to repair damage caused by chronic lung diseases such as COPD. The combined anti-inflammatory and reparative properties of stem cells can decrease lung inflammation, thereby reducing the inflammatory response in individuals with these types of diseases while restoring lung function.
Finally, I invite you to read our article “What Are Stem Cells?“