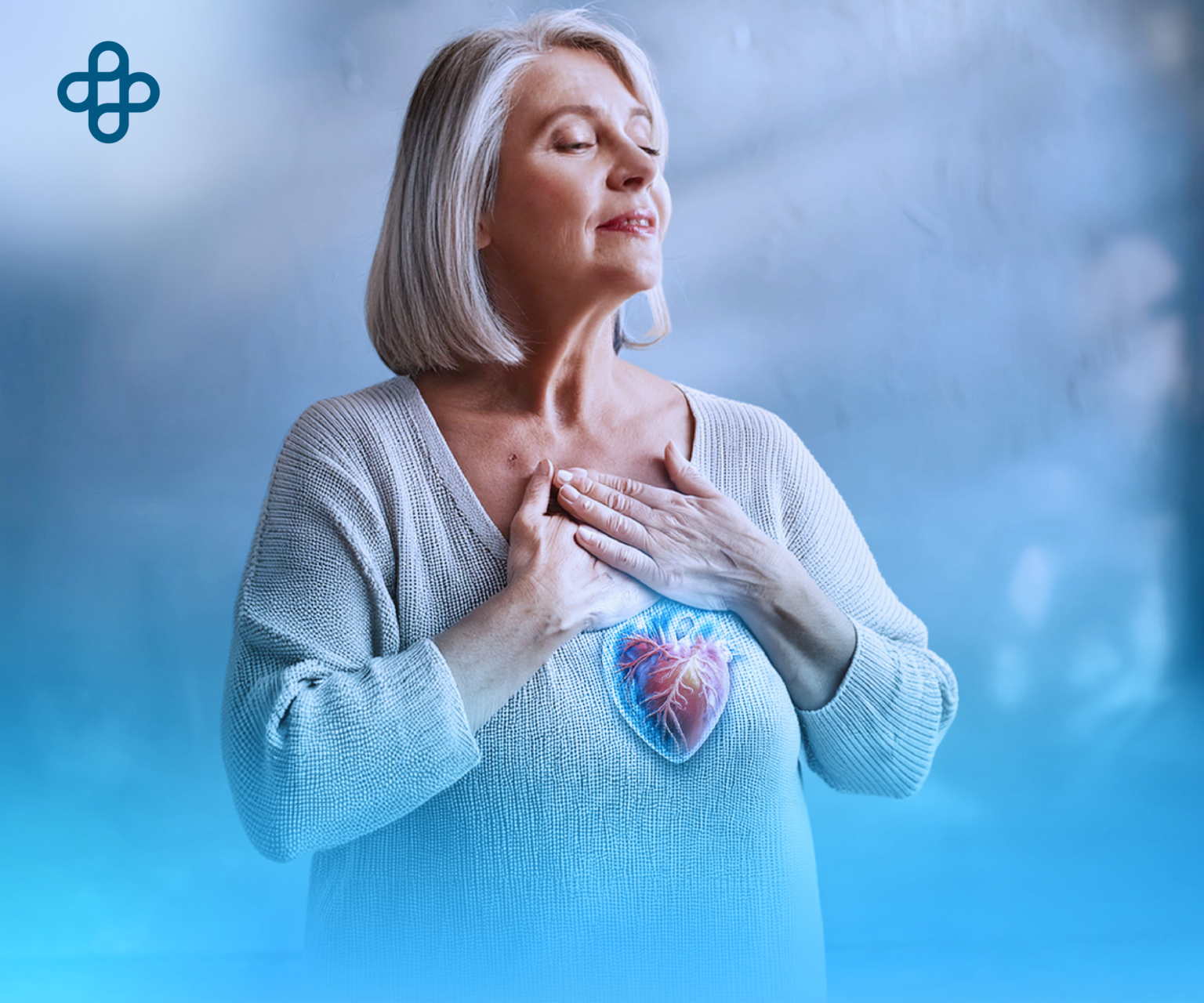
Enhance heart health with stem cells. Cardiovascular health is essential for a vibrant and healthy life. Today, heart disease remains one of the leading causes of death globally, underscoring the importance of proactively caring for the cardiovascular system. An innovative and natural approach recently gaining traction is using stem cells to prevent and treat cardiovascular diseases.
What Are Stem Cells and How Can They Benefit the Heart?
Stem cells are unique cells capable of transforming into various tissue types. Among the most utilized in research and treatments are mesenchymal stem cells and those derived from umbilical cord blood. Their remarkable regenerative potential makes them a pivotal tool in regenerative medicine.
In cardiovascular contexts, stem cells are primarily used to regenerate damaged tissues, such as heart muscle post-infarction. They also support improved blood circulation and reduce inflammation, two crucial factors in heart health.
Key Benefits of Stem Cell Therapy for Cardiovascular Health
Scientific studies reveal that stem cells provide several essential benefits for heart health:
- Heart Tissue Regeneration: In cases of heart failure or muscle damage, stem cells help repair damaged areas, enhancing heart function.
- Improved Blood Circulation: Stem cells promote new blood vessel formation, improving blood flow to heart tissue and lowering the risk of future complications.
- Inflammation Reduction: Chronic inflammation poses a significant risk in heart disease. Stem cells possess anti-inflammatory properties that reduce inflammation in arteries and affected tissues.
- Atherosclerosis Prevention: This condition, characterized by plaque buildup in the arteries, can lead to severe events like heart attacks. Stem cells help prevent this process by reducing inflammation and promoting vascular health.
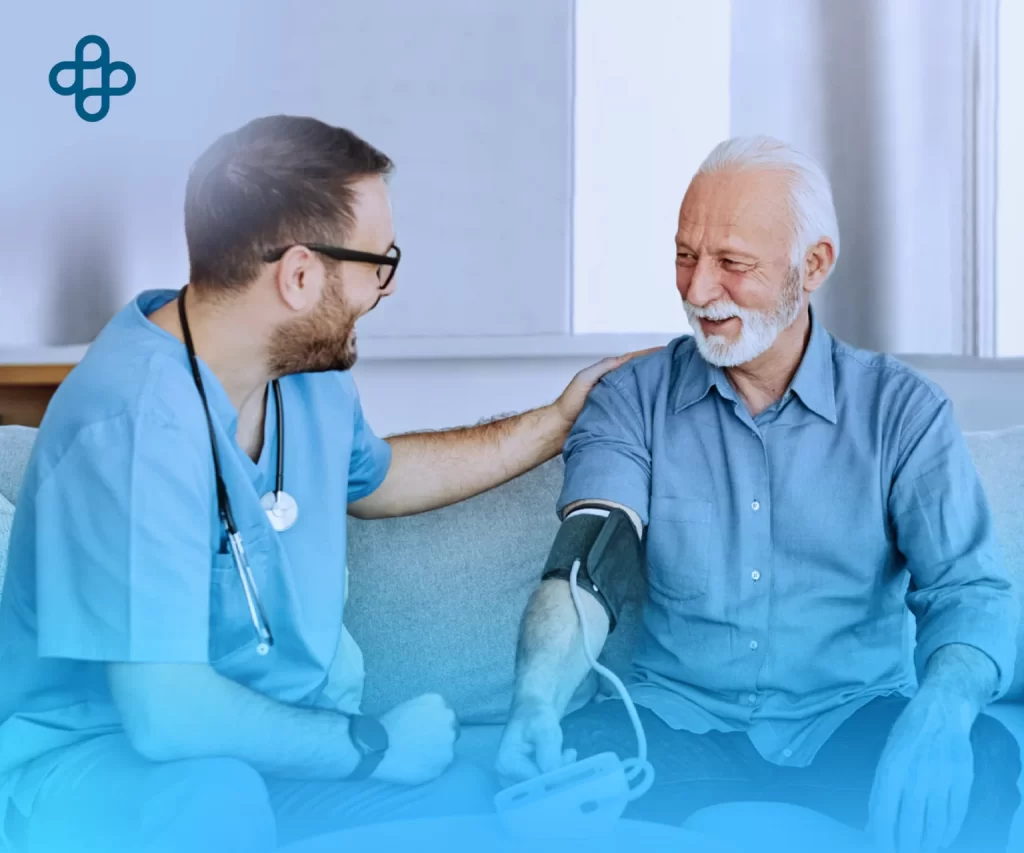

Advances in Stem Cell Therapy for Cardiac Health
Research in using stem cells in cardiology has progressed significantly in recent years. In a 2022 study published in Nature Reviews Cardiology, scientists found that mesenchymal stem cells substantially improved left ventricular function in post-myocardial infarction patients. This breakthrough indicates that stem cells contribute to tissue regeneration and positively impact patients’ long-term quality of life.
Additionally, a clinical trial published in The Journal of the American College of Cardiology reported that using bone marrow-derived stem cells in heart failure patients reduced mortality by 25% compared to standard treatments.
Ideal Candidates for Stem Cell Therapy
While promising, not all cardiovascular patients are ideal candidates for stem cell therapies. Patients with extensive heart tissue damage or those who have suffered multiple cardiac events may benefit most. However, individuals with risk factors like diabetes or hypertension may not respond optimally.
Interested patients must consult a regenerative cardiology specialist to determine if this therapy suits them. As research progresses, these therapies are expected to become more accessible and applicable to a broader range of individuals.
The Future of Natural Stem Cell Therapies in Cardiology
Stem cell treatments for cardiovascular diseases are revolutionizing medicine. As research continues to confirm their safety and efficacy, clinical use will likely expand to include tissue regeneration and the prevention of cardiovascular diseases in high-risk individuals.
Researchers are exploring combining stem cell therapies with conventional treatments, such as medication for hypertension or cholesterol, to maximize outcomes. This synergy between regenerative medicine and traditional pharmacology could herald a new era in heart disease treatment.
Conclusion – Enhance heart health with stem cells
Enhancing cardiovascular health naturally is possible through regenerative medicine advancements and the use of stem cells. This approach promises improved quality of life for millions by repairing damaged tissues and preventing future heart problems. However, as with any innovative treatment, consulting with specialists is essential to determine if this therapy is suitable for each patient.