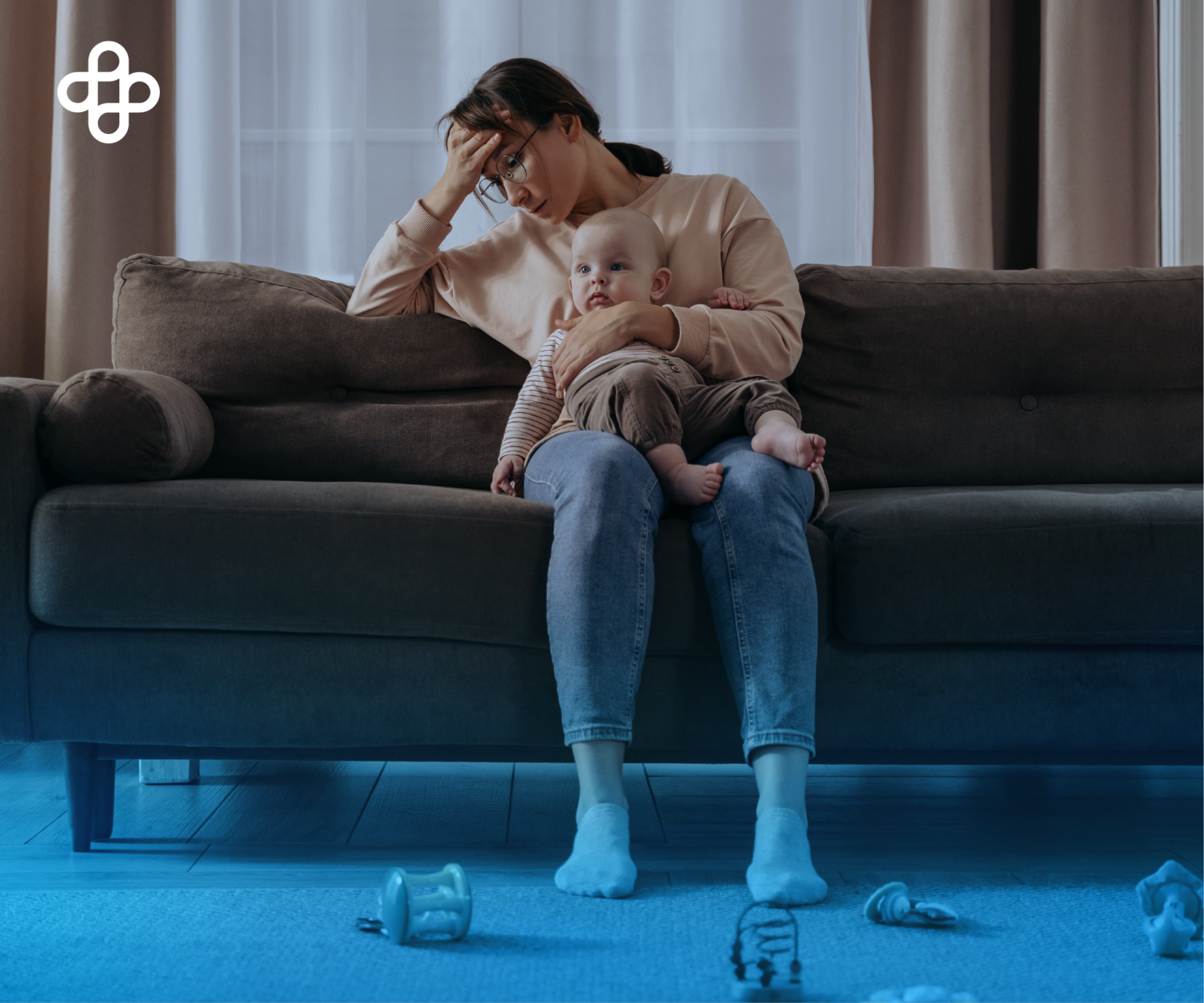
Symptoms of depression and anxiety.
When Should You Be Concerned About Anxiety or Depression?
Firstly, Do you struggle with daily tasks? Secondly, Do you worry excessively about minor things? Thirdly, Do you experience persistent tension, like a tight knot in your stomach, lasting for days? If so, it may be time to evaluate whether you are suffering from anxiety or depression.
According to the National Health Service (NHS) of the UK, anxiety is a natural response of the human body, closely linked to the “fight or flight” reaction—an instinctual survival mechanism seen in animals facing threats in nature.
When the body perceives danger, the nervous system and hormones react by:
- Increasing heart rate
- Heightening alertness
- Releasing adrenaline
However, the problem arises when these responses become excessive and persistent.

What Causes Anxiety Disorders?
Anxiety can be triggered by various factors, including:
- Environmental stressors (work pressure, family conflicts)
- Genetics (family history of anxiety or depression)
- Psychological factors (trauma, low self-esteem)
- Developmental experiences (childhood neglect, bullying)
- Specific life events (illness of a loved one, job loss, violence, public embarrassment)
In some cases, individuals cannot pinpoint the cause of their anxiety, or they may recognize their worries as irrational but still feel powerless to control them.
“Anxiety becomes pathological when it interferes with daily life, causing distress, emotional suffering, and a decline in quality of life.”
– Gabriela Bezerra de Menezes, UFRJ Researcher
Anxiety vs. Depression: What’s the Difference?
Both anxiety and depression negatively impact daily life and are considered severe mental health conditions. Although they often occur together, they have distinct symptoms and require different treatments.
| Anxiety | Depression |
|---|---|
| Characterized by constant fear, worry, and distress | This leads to persistent sadness, hopelessness, and a lack of motivation |
| Hyperactive, restless behavior | Low energy, fatigue, and slow movements |
| Racing thoughts and excessive worrying | Difficulty thinking, concentrating, and making decisions |
| Physical symptoms like rapid heartbeat, sweating, dizziness | Changes in appetite, sleep, and energy levels |
| Tendency to avoid situations that cause distress | Loss of interest in previously enjoyable activities |
Symptoms of Depression
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), depression is characterized by a persistent low mood (sadness, irritability, or emptiness) and a loss of interest in activities for at least two weeks.

Additional symptoms may include:
- Irritable or low mood most of the time
- Difficulty sleeping or excessive sleep
- Significant changes in appetite (leading to weight gain or loss)
- Fatigue and low energy levels
- Feelings of worthlessness, self-hate, or excessive guilt
- Difficulty concentrating
- Slowed or agitated movements
- Withdrawal from social activities
- Hopelessness or feelings of abandonment
- Recurring thoughts of death or suicide
- Loss of pleasure in hobbies, socializing, or sexual activity
Symptoms of Anxiety
Anxiety symptoms vary but often include:
- Intrusive, uncontrollable anxious thoughts: Persistent worry that disrupts daily life and worsens over time
- Physical symptoms:
- Rapid or strong heartbeat
- Unexplained body aches and pains
- Dizziness or shortness of breath
- Behavioral changes: Avoiding activities or situations that trigger anxiety
How Can You Manage Anxiety and Depression?
If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of anxiety or depression, seeking professional help is essential. Treatment options include:
- Therapy (CBT, counseling, support groups)
- Medications (antidepressants, anxiolytics)
- Lifestyle changes (exercise, sleep, nutrition)
- Mindfulness and relaxation techniques
Want to learn about cutting-edge treatments?
Explore how stem cell therapy is being researched for depression in our article: Depression: Symptoms, Causes, and Effective Treatments You Need to Know