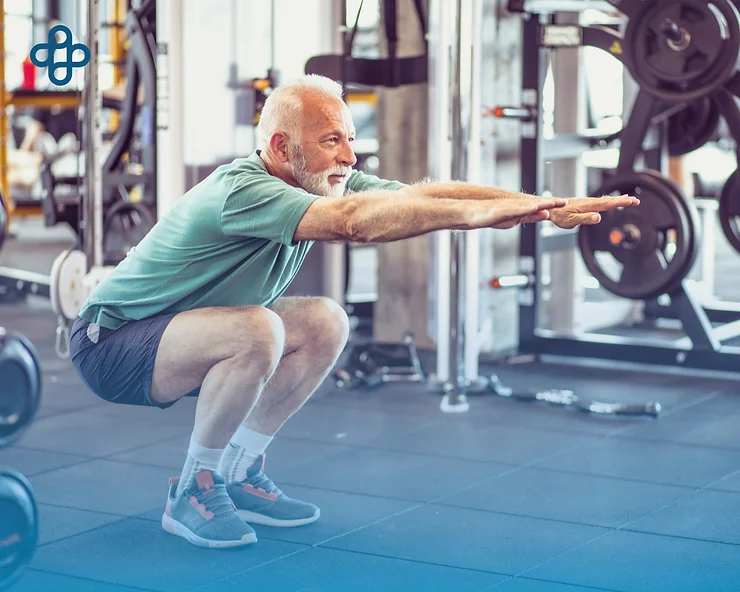
Treatment of osteoporosis includes medication, a healthy diet, and weight-bearing exercises to prevent bone loss or strengthen weak bones.
The most common osteoporosis treatments include:
Calcium and Vitamin D:
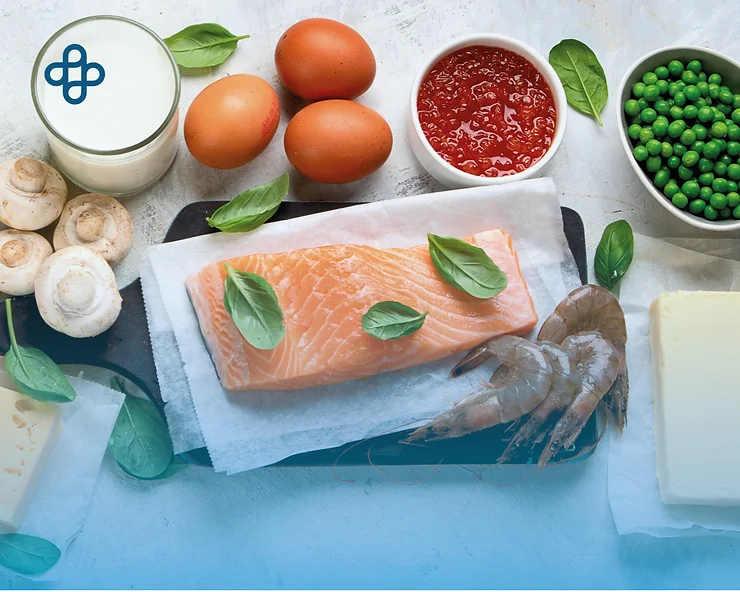
Osteoporosis treatment starts by ensuring the proper absorption of calcium and vitamin D, as this vitamin is essential for the body to adequately absorb calcium. Calcium: It is a nutrient, so the best way to ingest it is through food. You can easily obtain most of the calcium through milk and dairy products. It is advisable to have a calcium intake of around 1 gram per day in most cases. Vitamin D: Its content in foods is very low, except in some fatty fish, so the best way to acquire it is through sun exposure prudently. People with vitamin D deficiency may require higher doses.
The food you eat can affect your bones. Learning about the foods that are rich in calcium, vitamin D and other nutrients that are important for your bone health and overall health will help you make healthier food choices every day.
Bone Health and Osteoporosis Nutritional Guide
Weight-bearing exercises:
Weight-bearing exercises like walking, climbing stairs, and dancing increase bone mineral density. Most experts recommend doing 30 minutes of weight-bearing exercise per day.
Medications:
These drugs reduce bone resorption. They are especially indicated in cases of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Doctors use estrogens and selective estrogen receptor modulators, such as raloxifene, in these cases.
Lifestyle modification:
This includes avoiding immobility and engaging in sports. Sports are very important for increasing bone mass during growth and can help reduce the loss of bone mass in elderly people. It also has other benefits: it increases flexibility, coordination, and muscle strength.
Medication selection will depend on the patient’s characteristics. Experts stress that consistent treatment over several years is necessary for it to be effective.
The drugs currently used to treat osteoporosis manage to stop bone resorption and prevent mineral loss.
These are known as resorption inhibitors and include estrogens, calcitonin, bisphosphonates (etidronate, alendronate, and risedronate), selective estrogen receptor modulators (raloxifene), and even statins, drugs initially used to combat cholesterol.
Although pharmacological treatment is very important, it is also important to follow the measures mentioned above to correct nutritional deficiencies and improve lifestyle, which can prevent falls and minimize the disease’s impact.

Causes of Osteoporosis
Nutritional deficiencies
As mentioned earlier, it is most important that the patient takes the necessary amounts of calcium and vitamin D.
Regarding calcium, being a nutrient, the best way to ingest it is with food. Most calcium is obtained through milk and dairy products.
The vitamin D content of foods is very low, except for some fatty fish, so the best way to acquire this vitamin is through moderate sun exposure.
Elderly patients usually do not expose themselves to the sun, so they often need to take vitamin D supplements to ensure they meet their daily requirements.
Other nutritional elements
In addition to monitoring calcium and vitamin D intake, the patient should ensure they consume the appropriate proportion of basic nutrients, vitamins, and trace elements, such as magnesium. “They should avoid vitamin A supplements, as they have been shown to increase the risk of fracture,” they add.
Osteoporosis Treatment
Regarding hyperproteic diets and those rich in sodium and phosphorus, there is currently controversy over whether they should be avoided or not, as they increase urinary calcium excretion due to tubular reabsorption.
Final Recommendation
The content of this article aims to guide and instruct you in a general way about this disease. However, it is essential to seek medical treatment when suspecting the presence of the disease.
If you want to learn more, visit our article on What Are Stem Cells?