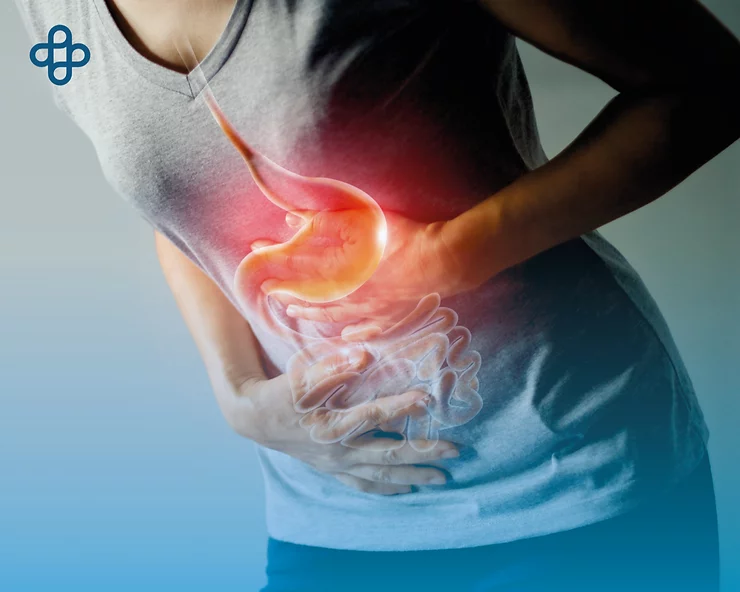
Colitis, an inflammatory condition of the colon’s lining, arises from a variety of causes, with the most common being infections or viruses, loss of blood supply, chronic diseases, and allergic reactions.
What is Colitis?
Colitis refers to inflammation within the lining of the colon, triggered by numerous conditions, notably ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease—both forms of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD). The inflammation results as a response to harmless bacteria and molecules found in foods.
Being often a lifelong condition without a cure, colitis requires management through various treatment options to control symptoms. It typically emerges in individuals aged 15 to 35 years or 55 to 70 years.
Understanding the Causes of Colitis
While the exact cause of colitis remains elusive, it’s essential to recognize the diversity of this condition, where inflammation can stem from several factors:
- Infections: Acute and/or chronic infections by viruses, bacteria, toxins, and/or parasites, including food poisoning.
- Inflammatory Disorders: Conditions like ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease may arise from infectious agents mistakenly activating the immune system, allergic reactions, stress, or environmental factors. Ulcerative colitis is marked by inflammation and ulceration within the colon’s inner wall.
- Ischemic Colitis: Caused by inadequate blood flow.
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): Characterized by intestinal rhythm changes, inflammation, abdominal pain, gas, nausea, and vomiting, also known as nervous colitis, often linked to high stress or anxiety levels.
- Radiation Therapy: Directed at the large intestine for cancer treatment.
- Medication: Certain drugs, such as antibiotics and anti-inflammatories, can inflame the colon’s mucosa, leading to pseudomembranous colitis.
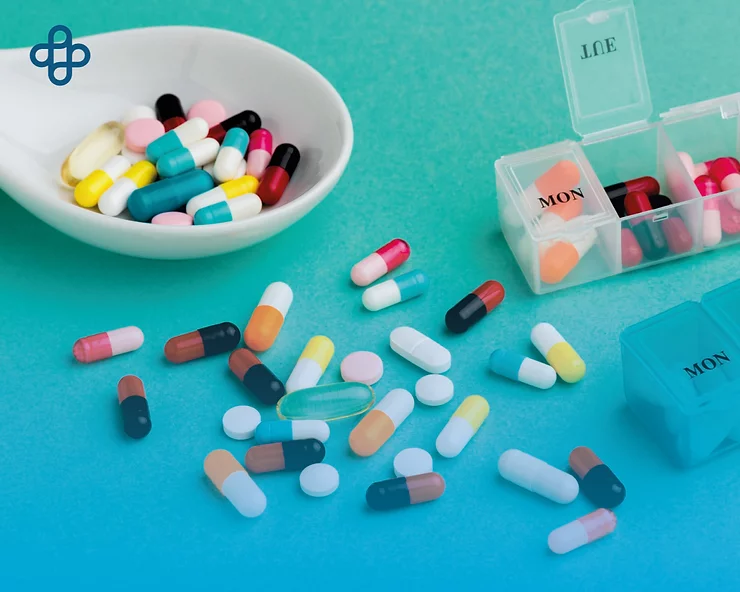

Summary – Colitis Causes
According to an NIH article, colitis causes are frequently unidentified, potentially including:
- Infections: From viruses or parasites.
- Food Poisoning: Due to bacteria.
- Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis: Specific types of IBD.
- Ischemic Colitis: From reduced blood flow.
- Radiation: To the large intestine causing radiation enteritis and colitis.
- Necrotizing Enterocolitis.
- Pseudomembranous Colitis: Triggered by Clostridium difficile infection.
Inflammation of the colon’s inner lining, known as colitis, can result from various conditions, with ulcerative colitis being the most prevalent. Consulting a doctor is crucial for anyone suspecting they might have colitis.
In conclusion, incorporating transition words effectively enhances the readability and coherence of the text, making it more engaging for the reader. By following these guidelines, individuals can take proactive steps toward preventing colitis and managing the symptoms of inflammatory bowel disease.
Finally, If you want to know more, visit our article on What Are Stem Cells.