A blood stem cell transplant is a medical procedure used to treat individuals with potentially life-threatening diseases. Experts technically call this type of transplant a hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT). You might also encounter it under the names:
- Bone marrow transplant
- Stem cell transplant (or peripheral blood stem cell transplant)
- Umbilical cord blood transplant
What are Blood or Hematopoietic Stem Cells?
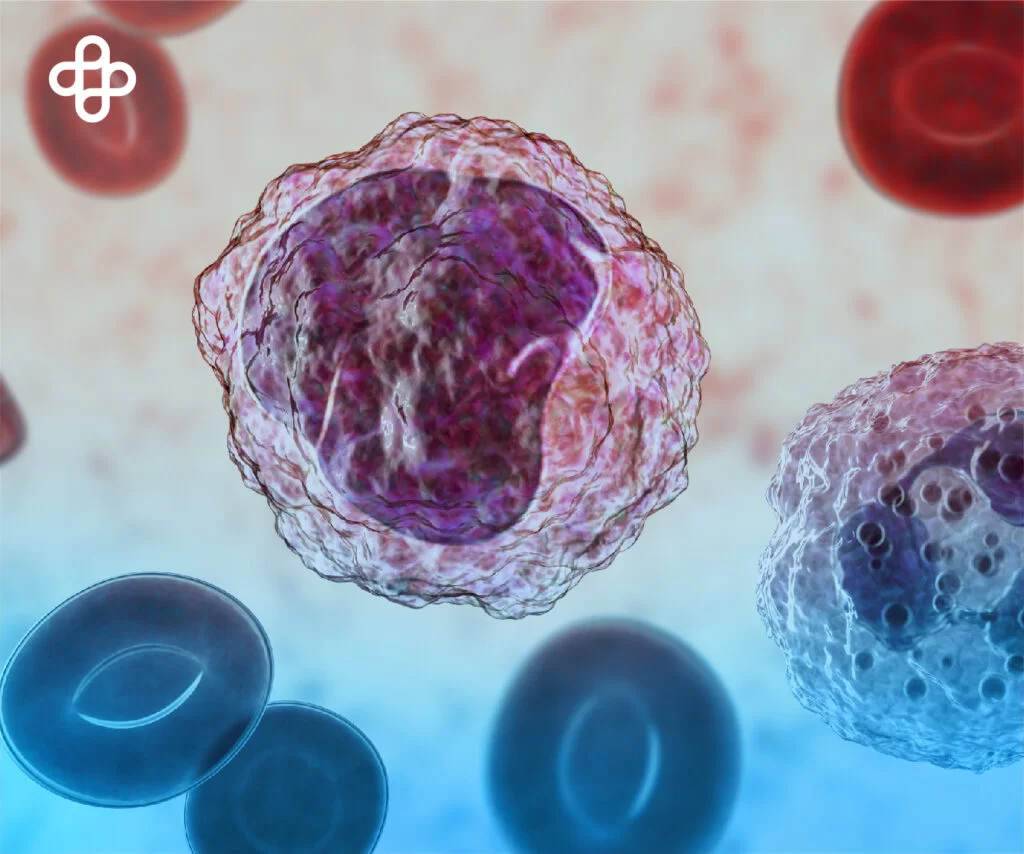
Blood stem cells are special cells that allow our body to produce:
- White blood cells, essential for fighting infections
- Red blood cells, which carry oxygen to our body’s cells and remove waste products
- Platelets, which enable blood clotting
The spongy tissue inside our bones, known as bone marrow, contains blood stem cells. They are also present in the placenta and umbilical cord blood of newborns.
Who Needs a Bone Marrow, Stem Cell, or Umbilical Cord Blood Transplant?
Sometimes, blood stem cells in the bone marrow don’t function correctly and start producing:
- Too many blood cells
- Too few blood cells
- Abnormal blood cells
This condition may require a blood stem cell transplant to correct it.
The National Cancer Institute explains that for patients with certain types of cancer, the most effective treatment may involve very high doses of chemotherapy or total body irradiation. This treatment destroys not only diseased cells but also blood cells. A stem cell transplant may be necessary to “rescue” the patient from this potentially life-threatening side effect.
Transplants can also be a therapeutic option for patients with certain hereditary diseases, such as immunodeficiency.

Types of Blood Stem Cell Transplants
There are several types of transplants, depending on the origin of the stem cells:
- Bone marrow transplants (BMT): Specialists extract stem cells from the bone marrow.
- Peripheral blood stem cell transplants (PBSCT): Specialists extract stem cells from the bloodstream.
- Umbilical cord blood transplants (UCBT): Stem cells are extracted from the placenta and umbilical cord of a newborn.
The type of transplant also varies based on the source of the cells:
- Autologous transplants: Use previously extracted cells from the patient.
- Allogeneic transplants: Use cells provided by a donor.
- Syngeneic transplants: Use cells from an identical twin.
Before the transplant, patients receive high doses of chemotherapy or radiotherapy to destroy the disease and make space for the new, healthy cells.
- When the chemotherapy or radiotherapy dose completely suppresses the patient’s immune system, doctors refer to the procedure as a myeloablative transplant.
- When a patient receives less intensive doses of chemotherapy or radiotherapy, doctors call the procedure a reduced-intensity or non-myeloablative transplant.
Visit our article on “What are Stem Cells?”