Regenerative medicine for arthritis pain relief: A Breakthrough for Arthritis Sufferers
Regenerative medicine is revolutionizing the treatment of arthritis, offering new hope to those suffering from this painful condition. This cutting-edge approach uses the body’s cells to repair and regenerate damaged tissues, reducing pain and improving mobility. This article will explore how regenerative medicine can alleviate arthritis pain and the various available methods.
What is Regenerative Medicine?
Regenerative medicine focuses on repairing, replacing, or regenerating cells, tissues, and organs to restore normal function. It employs various techniques, including cellular therapy, tissue engineering, and molecular regenerative medicine. These therapies have the potential to significantly change the treatment landscape for many chronic diseases, including arthritis.
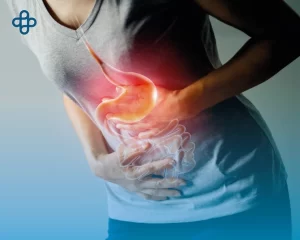
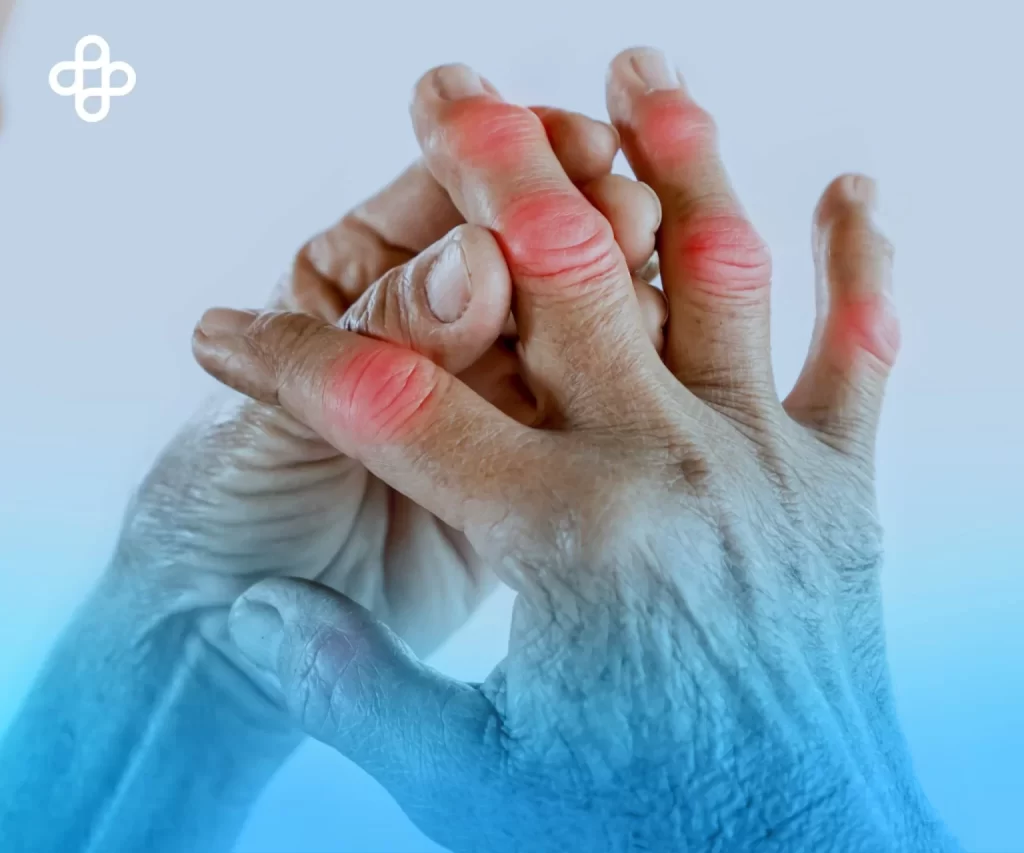
Arthritis: A Common Ailment
Arthritis affects millions worldwide, causing joint pain, inflammation, and stiffness. The most common forms are osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. While traditional treatments, such as anti-inflammatory medications and physical therapy, can relieve symptoms, many patients seek longer-lasting and less invasive solutions.
Alleviating Arthritis Pain
Cellular Therapies: The Key to Recovery
One of the most promising regenerative medicine techniques for arthritis is cellular therapy. This treatment involves injecting stem cells into the affected joints. Stem cells have the unique ability to differentiate into various cell types, helping to repair damaged tissue. Studies have shown that these therapies can significantly reduce pain and improve joint function.
Types of Stem Cells Used
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs): MSCs, which are located in bone marrow, adipose tissue, and umbilical cord tissue, differentiate into cartilage and bone cells.
- Hematopoietic Stem Cells (HSCs): Located in the bone marrow, HSCs can differentiate into various blood cell types and have anti-inflammatory properties beneficial for arthritis.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP): A Natural Approach
Another increasingly popular regenerative technique is platelet-rich plasma (PRP). This treatment involves extracting a patient’s blood, concentrating the platelets, and injecting the PRP into the affected joints. Platelets contain growth factors that can accelerate the repair of damaged tissues and reduce inflammation and pain.
Benefits of PRP Therapy
- Pain Reduction: Many patients report significant pain relief following PRP treatment.
- Improved Joint Function: PRP can help restore mobility and joint function affected by arthritis.
- Minimally Invasive Procedure: Using the patient’s blood minimizes the risk of adverse reactions.

Tissue Engineering: Creating New Solutions
Tissue engineering, another branch of regenerative medicine, offers innovative solutions for arthritis. This approach involves creating new tissues in the lab that can be implanted into damaged joints. Advances in this field have led to the development of biological scaffolds that support the growth of new cartilage and bone.
How Does It Work?
- Biocompatible Scaffolds: These scaffolds are made from materials compatible with the human body and can be absorbed over time.
- Growth Factors: Scaffolds can be impregnated with growth factors to stimulate tissue regeneration.
- Stem Cells: Stem cells can be seeded onto the scaffolds to promote the formation of new cartilage tissue.
The Future of Regenerative Medicine in Arthritis Treatment
The field of regenerative medicine is constantly evolving, with researchers continuously exploring new ways to treat arthritis. Promising results are emerging from ongoing clinical trials, and as a result, more effective and accessible treatments will likely follow. Soon, these advancements could revolutionize arthritis care, ultimately improving the quality of life for many patients.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the promise of regenerative medicine, several challenges remain. The active research areas are standardizing procedures, ensuring long-term safety, and improving effectiveness. Additionally, the high cost of these treatments may be a barrier for some patients, highlighting the need for healthcare policies that make these therapies more accessible.
Conclusion
In conclusion, regenerative medicine opens new doors for arthritis treatment, offering patients options to reduce pain and improve their quality of life. With continued advancements in cellular therapy, PRP, and tissue engineering, the future looks bright for those suffering from this debilitating condition. By working closely with medical professionals, patients can explore these options and find a path to recovery and a life free of pain.
Stem Cell Advances in Arthritis Treatment: Insights from 2023 and 2024