Stem Cells and Vitiligo: Administering Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Vitiligo Can:
- Prevent further damage to melanocytes and reduce the progression of the disease.
- Substitute the cells that have disappeared as a result of the condition.
- Increase pigmentation over some time.
Scientists Obtain Melanocytes from Stem Cells
According to an article by Informed. French scientists have successfully obtained melanocytes capable of producing melanin. Melanin is essential for normal skin pigmentation and protection against ultraviolet rays from multipotent stem cells in vitro.
This achievement brings new hope for treating diseases such as vitiligo, albinism, and Waardenburg syndrome. The less common Griscelli syndrome, according to experts.

Stem Cells and Vitiligo
In 2009, the same team of researchers from the National Institute of Health and Medical Research (INSERM) managed to reconstitute a complete epidermis using embryonic stem cells. By obtaining keratinocytes (which constitute nearly 90% of the cells in the epidermis) first in vitro and then in mice, scientists paved the way for treating severe burns or skin ulcers resulting from diabetes.
Stem Cells in Vitiligo
Vitiligo is a disease of possible autoimmune etiology characterized by depigmented spots due to the loss of melanocytes, the cells responsible for skin pigmentation. Nowadays, it is necessary to demonstrate that these differentiated cells in vitro are functionally identical to their tissue counterparts.
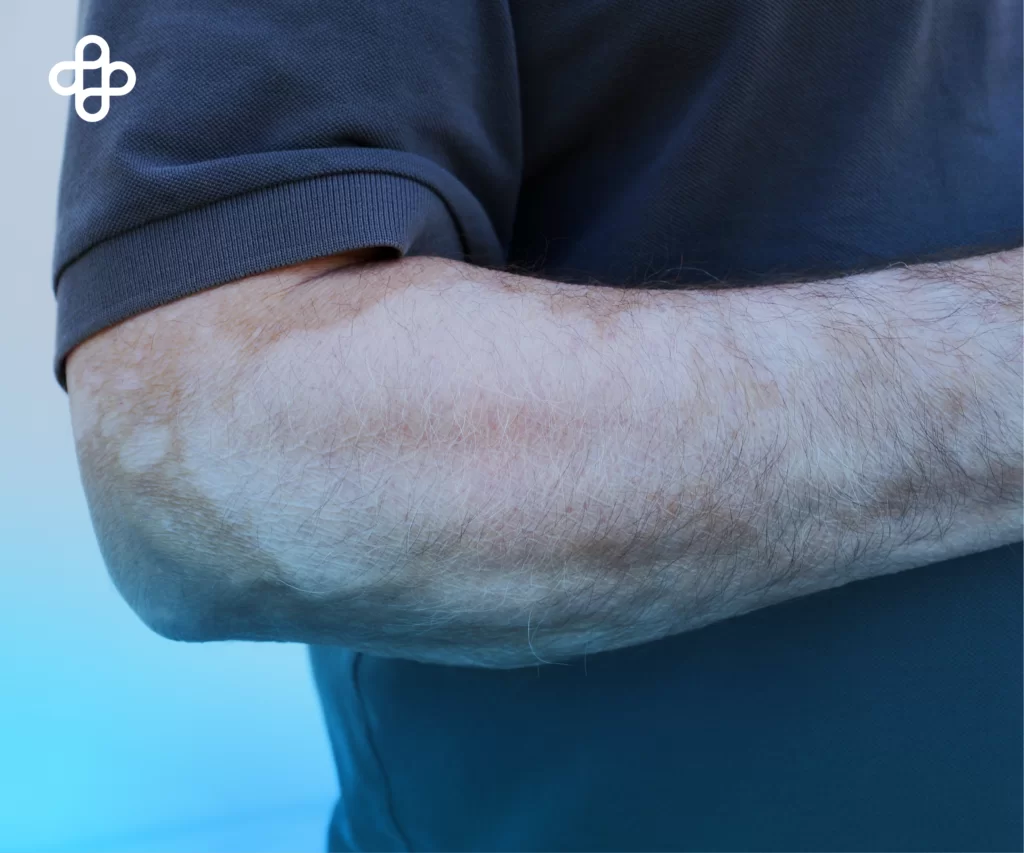
Stem Cells and Vitiligo
Autologous transplants of mixed cultures of melanocytes and keratinocytes have been used to treat vitiligo. This is because the interactions between these cells enhance the proliferation and migration of melanocytes. In vitro cocultures of adipose tissue-derived stem cells and melanocytes have also been studied, showing a decrease in differentiation and an increase in the proliferation and migration of melanocytes, albeit to a lesser extent than when cocultured with keratinocytes.
We invite you to read our article, “What Are Stem Cells?“





