How do we obtain stem cells? We obtain stem cells by collecting them from umbilical cord blood at the time of delivery. Scientists have developed different techniques to extract stem cells.
In general, scientists can directly extract both embryonic and adult stem cells from the site where they are found. Then, the culture stores them for a long time under special conditions.
Embryonic or fetal cells.
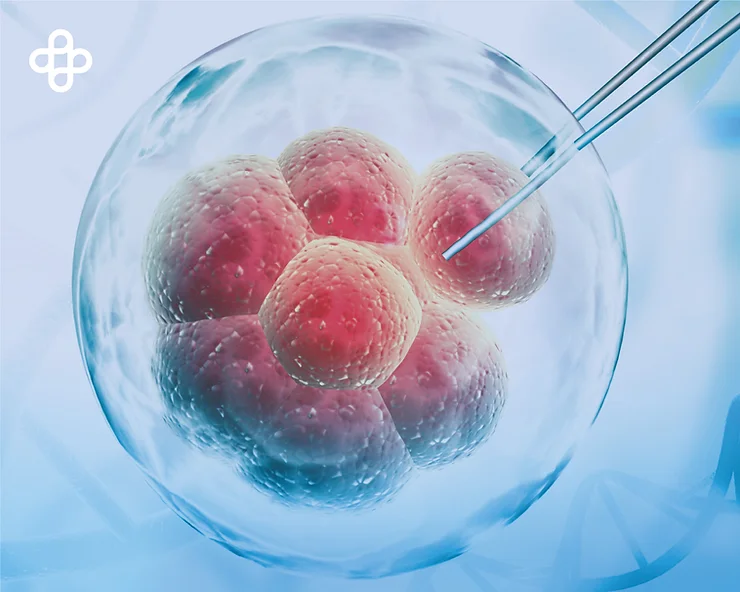
To obtain embryonic cells, scientists create embryos during in vitro fertilization processes. If these embryos are not used, they can be cryopreserved in liquid nitrogen.
Then, scientists extract embryonic cells from these cryopreserved embryos and culture them under special conditions to use them for research purposes.
Worldwide, this procedure is legal in almost all civilized countries. However, any use of fetal stem cells, including research, is prohibited. This is because the embryo may be damaged.
With this in mind, researchers have developed other techniques for their extraction to preserve the embryo completely intact. Experimentation so far has only been done with mouse embryos of up to 10 cells.
Only one of them has been extracted for culture. This has allowed the embryo to continue developing generally once it is implanted in the uterus of a female. The culture has enabled obtaining two normal and pluripotent cell lines.
Umbilical cord.
Someone collects umbilical cord blood for cryopreservation in private or public banks during childbirth. If necessary, they use it to treat the child itself or a direct relative for certain diseases in the first case.
On the other hand, it is available to donate to compatible people who may need it.
Somatic cell reprogramming.
Somatic cells are formed from embryonic stem cells. They are responsible for tissue development and cell renewal. Currently, a technique has been successfully tested that has allowed them to be genetically reprogrammed to become pluripotent stem cells.
For this purpose, the nucleus of an unfertilized egg cell is removed. This is replaced by a somatic cell, after which it reprograms itself to become a stem cell. The technique has already been tested in humans and has been used successfully in what is called therapeutic cloning.
These cells have the advantage of having the same genetic endowment as the patient, thus eliminating the possibility of rejection.
Other techniques
Scientists have developed another technique for this purpose, which makes it possible to generate what are known as induced pluripotent stem cells (IPS).
They use viruses as vectors to genetically reprogram somatic cells and transform them into pluripotent stem cells.
Cadaver donors. One can obtain adult stem cells from a person who has just died and preserve them by freezing them in liquid nitrogen.
Parthenogenesis. This process does not occur in humans, since it consists of the development of a living being from a single cell without fertilization. However, although it can only be performed in women, using chemical or physical methods, obtaining a mass of cells from which some pluripotential stem cells can be extracted.
I invite you to learn a little more about the subject by visiting our article What are stem cells?